Runs metaMS process for LC/MS feature annotation based on matching to an existing 'standards' DB. The figure below shows the main parts of this metaMS process.
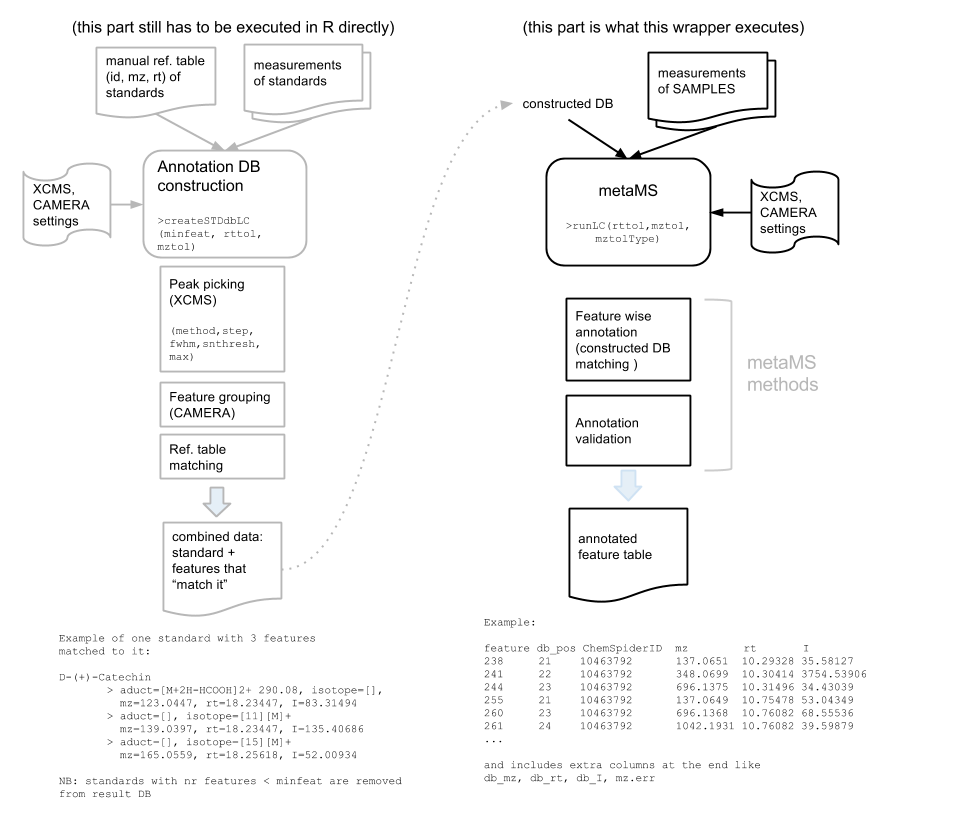
The implemented annotation strategy can be broken down in the following steps:
1. Feature wise Annotation: Each feature detected by runLC is matched against the database. If the mass error function is provided, the appropriate m/z tolerance is calculated, otherwise a fixed tolerance is used (mzdiff). The retention time tolerance is fixed and should be selected on the bases of the characteristics of each chromatographic method (rtdiff). Multiple annotations - i.e. features which are associated to more than one compound - are possible. This outcome does not indicate a problem per se, but is an inherent drawback of co-elution.
2. Annotation Validation: The annotated features are organized in 'pseudospectra' collecting all the experimental features which are assigned to a specific compound. A specific annotation is confirmed only if more than minfeat features which differ in retention time less than rtval are present in a pseudospectrum. As a general rule rtval should be narrower than rtdiff. The latter, indeed, accounts for shifts in retention time between the injection of the standards and the metabolomics experiment under investigation. This time can be rather long, considering that the standards are not commonly re-analyzed each time. On the other hand, rtval represents the shift between the ions of the same compound within the same batch of injections and therefore it has only to account for the smaller shifts occurring during peak picking and alignment.