What it does
This tool can be used to generate a bigWig or bedGraph file based on two BAM or CRAM files that are compared to each other while being simultaneously normalized for sequencing depth.
To compare the BAM files to each other, the genome is partitioned into bins of equal size, then the number of reads found in each BAM file is counted per bin, and finally a summary value reported.
The tool works in two steps: 1. Scaling : To properly compare samples with different sequencing depth, each bam file can be scaled either using the SES method (proposed in Diaz et al. (2012). "Normalization, bias correction, and peak calling for ChIP-seq". Statistical applications in genetics and molecular biology, 11(3).) or total read count. additionally scaling can be turned off and a per-sample normalization can be used (--normalizeUsing RPKM/CPM/BPM)
- Comparison : Two bam files are compared using one of the chosen methods (e.g. add, subtract, mean, log2 ratio etc.)
By default, if reads are from a paired-end sequencing run and reads are properly paired, the fragment length reported in the BAM file is used.
Note: For paired-end sequencing samples, each read mate is treated independently to avoid a bias when a mixture of concordant and discordant pairs are present. This means that _each end_ will be extended to match the fragment length.
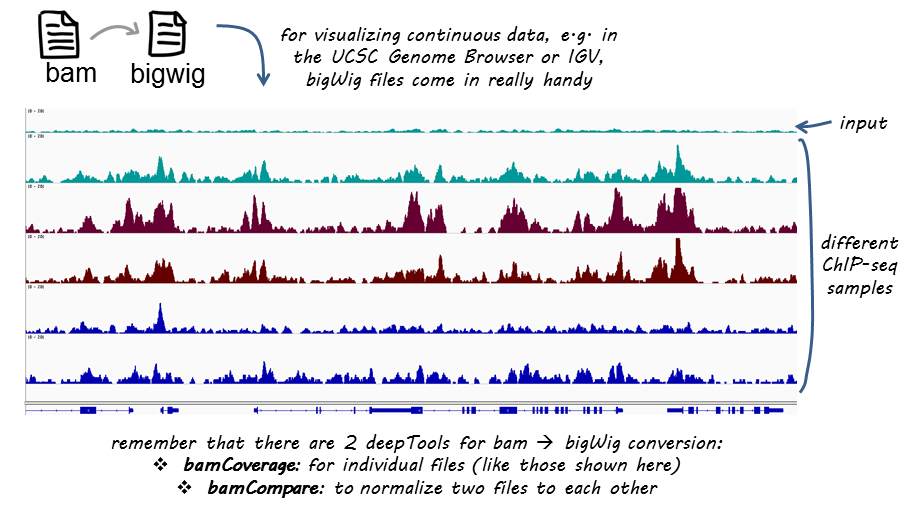
Output files
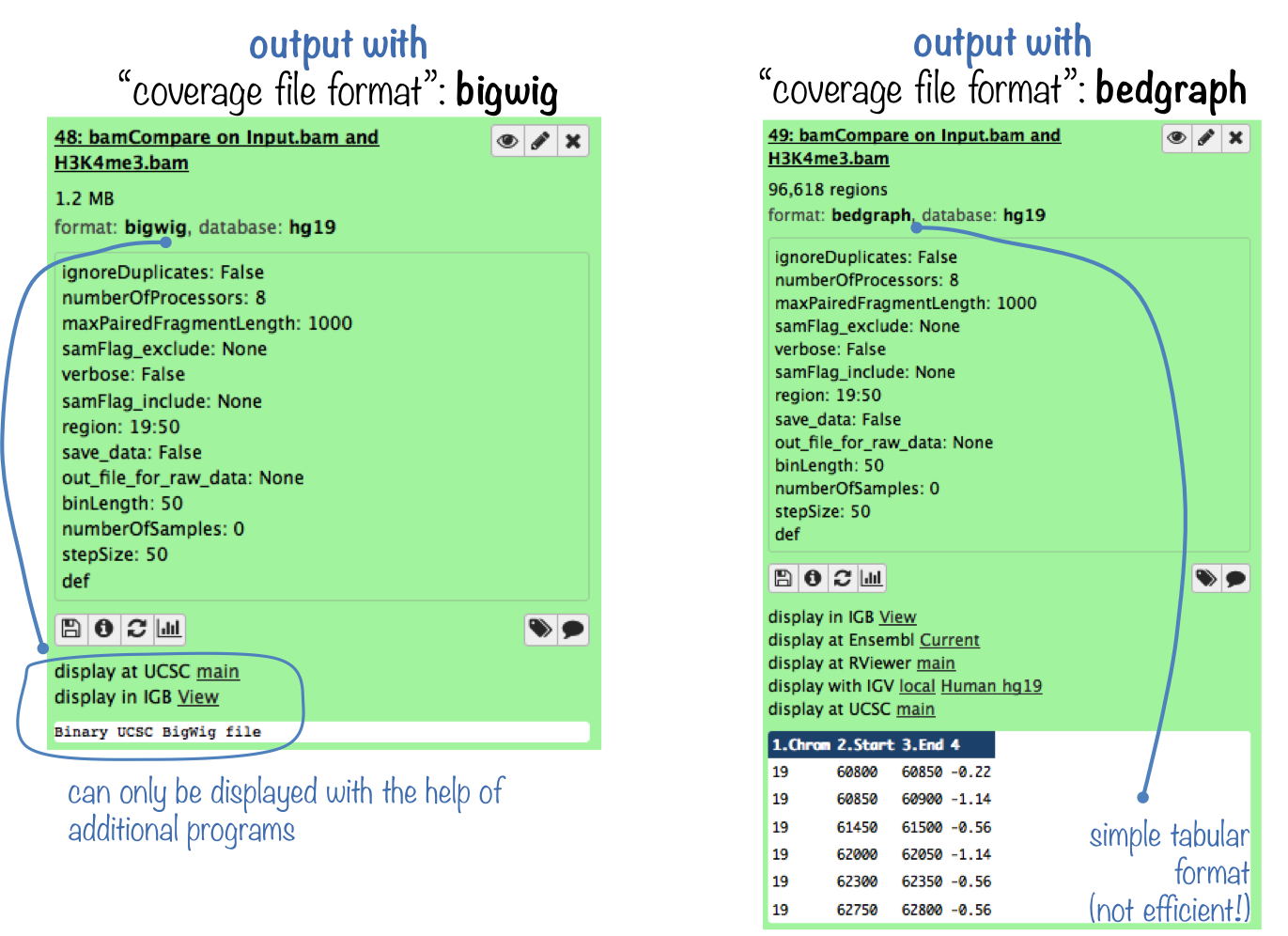
bamCompare produces the same kind of output as bamCoverage. The difference is that you now obtain 1 coverage file that is based on 2 BAM files: a bedGraph or a bigwig file containing the bin location and the resulting comparison values.
Like BAM files, bigWig files are compressed, binary files. If you would like to see the coverage values, choose the bedGraph output. For more information on typical NGS file formats, see our Glossary
For more information on the tools, please visit our help site.
For support or questions please post to Biostars. For bug reports and feature requests please open an issue on github.
This tool is developed by the Bioinformatics and Deep-Sequencing Unit at the Max Planck Institute for Immunobiology and Epigenetics.