
What it does
Single-linkage clustering on sequences.
Inputs/Outputs
Inputs
Sequences file:
The sequence file with all samples sequences (format FASTA). These sequences are dereplicated: strictly identical sequence are represented only one and the initial count is kept in count file.
The sequence ID must be "sequenceID;size=X" with X equal to the total abundance among all samples.
It corresponds to one output of FROGS Pre-process tools.
Count file:
This file contains the count of all uniq sequences in each sample (format TSV).
Example:
#id splA splB seq1 1289 2901 seq2 3415 0
Outputs
Abundance file (abundance.biom):
The abundance of each cluster in each sample (format BIOM). This format is widely used in metagenomic softwares.
Clusters seeds (seed_sequences.fasta):
The clusters representative sequences (format FASTA).
Clusters composition (swarms_composition.tsv):
A text file representing the read composition of each cluster (format txt). Each line represents one cluster and is composed of read identifier separated by space.
How it works
| Steps | With denoising | Without denoising |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sorting the reads by their abundance | Sorting the reads by their abundance |
| 2 | Clusters the reads (Swarm). The distance parameter is 1 | / |
| 3 | Sorting the pre-clusters by their abundance | / |
| 4 | Clusters the pre-clusters (Swarm) with the distance you specify | Clusters the reads (Swarm) with the distance you specify |
Swarm focus
Swarm use an iterative growth process and the use of sequence abundance values to delineate OTUs.
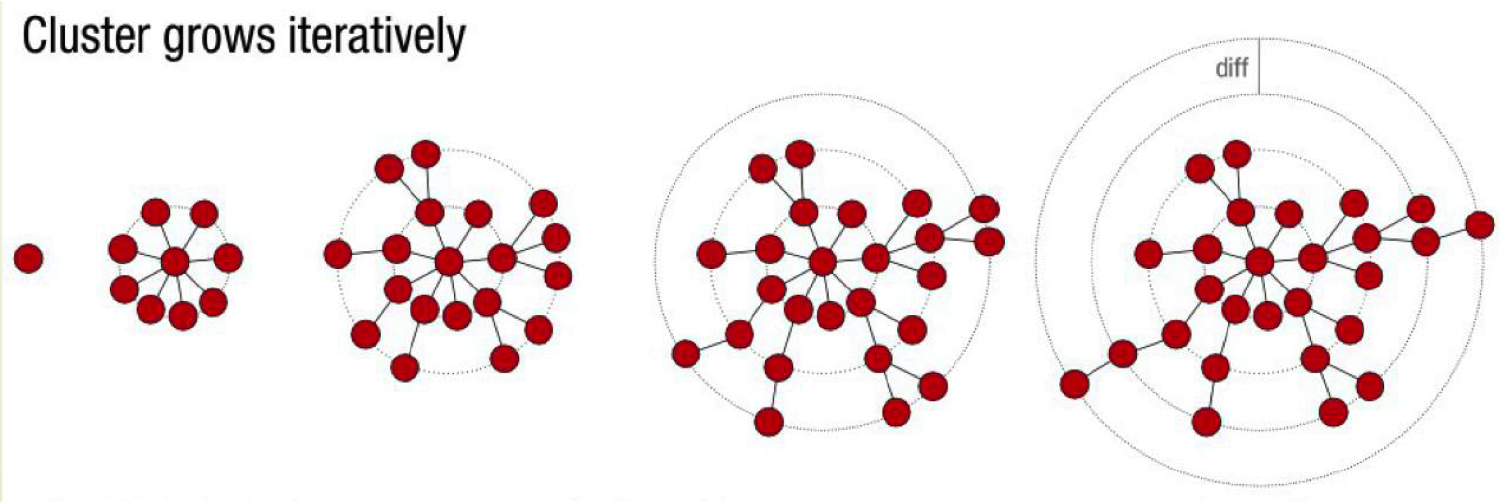
In each groth step the sequence of the previous step is used to find the others sequences with a number of differences inferior or equal to the "Aggregation distance".
After agregation Swarm refines the clusters by looking at the abundancies along the connections. Theoritically the abundances must decrease when you are going away from the seed (which is often the most abundant sequence). If this abundance raises again it means that two different clusters are connected by some poorly abundant sequences, so swarm cut the connection.
Advices
The denoising step allows to build very fine clusters with minimal differences. In this case, the number of differences is equal at 1 between sequences of each crowns. This first clustering is extremly quick. After the denoising, a second swarm is run with an aggregation distance >1 as you have configured, between seeds from this first clustering.
To have some metrics on your clusters, you can use the tool FROGS Clusters Stat.
Contact
Contacts: frogs@inra.fr
Repository: https://github.com/geraldinepascal/FROGS website: http://frogs.toulouse.inra.fr/
Please cite the FROGS article: Escudie F., et al. Bioinformatics, 2018. FROGS: Find, Rapidly, OTUs with Galaxy Solution.